Businesses are always looking to grow and diversify their revenue streams through additional income streams in today’s digital economy. Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) business models bring in revenue that can help you increase your market share and accelerate the growth of your business.
When launching a business, it is important to identify a sustainable revenue and business model that will not crash and burn the moment your product or service becomes popular or the economy changes. One of the easiest ways to ensure long-term success is by identifying lucrative Buy Now Pay Later models to ensure your business remains solvent as you continue to grow.
BNPL business models are great opportunities to grow your business in no time. According to Allied Market Research, the global BNPL market size will be worth 3.98 trillion dollars by 2030! If you implement them right into your business model, your business can benefit immensely from Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL) models. These models have become popular in developing countries and are gaining traction globally.
You might have heard of companies like AfterPay, Affirm, Lazypay, Simpl, Slice and many more that provide Buy Now, Pay Later services to their clients and earn profits via interest on the loans they provide. If you want to know more about this lucrative business model, keep reading this post!
Content Index:
- BNPL market overview
- BNPL payment modes
- BNPL distribution channels
- Buy Now Pay Later business models
- Tips for businesses to grow using BNPL
- FAQs
BNPL market overview
A report by HSIE Research by HDFC Bank said India’s Buy-Now-Pay-Later (BNPL) market is positioned as a source of rapid growth and massive scale. It is estimated that the BNPL market can grow to $56bn by 2026. BNPL revenue models are a way for businesses to appeal to customers who may not be able or willing to pay for their products upfront.
India’s BNPL market size was about USD 9 billion in 2020 and has been growing rapidly at a 28% CAGR from FY21E. It will touch $56 billion by FY26E, making India the largest P2M (peer to merchant) payment market. When coupled with fintech innovation, the BNPL market represents a major opportunity to expand access to credit and sustain economic activity.
- According to Allied Market Research, the current global BNPL market size is worth $90.69 billion.
- According to Precedence Research, the global buy now pay later market size reached $125.09 billion in 2021.
- The market size is expected to reach USD$3.98 trillion by FY30.
- In Sweden, it has almost become standard for eCommerce stores to offer BNPL as a payment option because of its growing popularity there; about 50% of Swedes choose to shop online using it, making up a third of all Swedish payments.
- According to one survey, 50% of US consumers have used BNPL at least once in their lifetime.
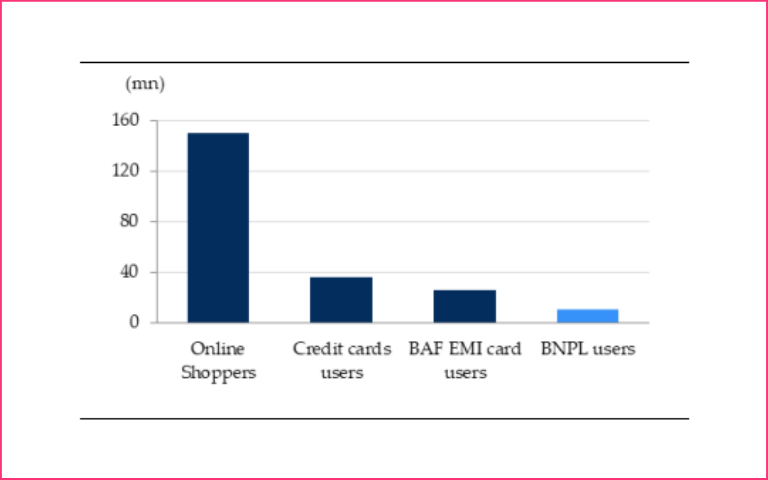
- BNPL’s user base in India at present is ~1/3rd of credit card users. In the last two years, as many as 30 players have launched the BNPL business model to take advantage of large opportunities.
Source: CIBIL, HSIE Research
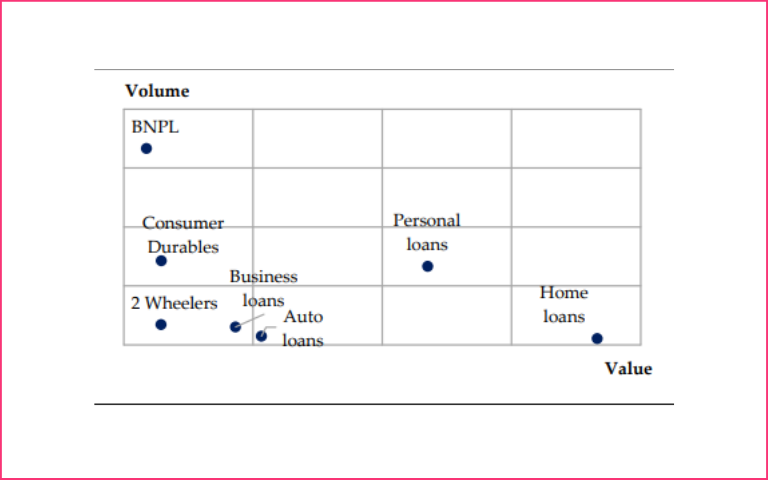
- BNPL is high on volumes but low on outstanding loans.
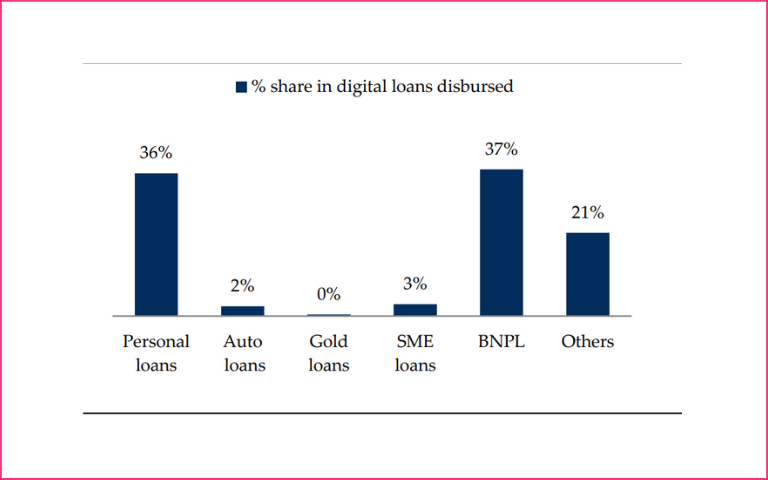
- According to data from RBI. and HSIE research, BNPL contributed to ~37% of retail digital lending by banks by volume in FY20.
BNPL payment mode and distribution channels
BNPL is a payment method, usually involving instalment plans or deferred billing agreements, allowing consumers to obtain goods and services on credit terms. The buyer’s payments are deferred according to a pre-established schedule until a future date (typically two to three months after service delivery) when they become due. Many businesses offer BNPL options as their primary business model, although it can also be used in conjunction with other payment methods.
BNPL payment modes
Pay Later:
Pay later is a type of payment where a customer can pay at a future date (e.g. 12 months). Customers can buy goods or services using BNPL while they spend on an instalment basis. The cost of goods/services will be divided into several monthly instalments with no interest applied. Customers will repay through regular deductions from their bank accounts or cash payments.
Split Pay:
Split Pay means customers make the initial payment to initiate service. For example, if you purchase something for ₹ 2000/- or above, it would be split into monthly instalments of say ₹1000/-. So you would pay ₹ 2000 initially and the rest of ₹ 1000 in your next instalment.
APR (Long-term financing at 0% Annual Percentage Rate):
This is similar to regular instalment plans but with a significantly longer repayment term ranging from 1 to 5 years.
Longer-term financing with subsidised interest or fees:
An eCommerce platform can offer customer loans with an interest rate lower than bank rates. This is very similar to the Split Pay model, but it does not require any credit checks upfront. While the standard payment model requires credit checks, instalments do not require any.
BNPL distribution channels:
Merchant checkout:
Merchant checkout is common for B2C e-commerce sites, but it is also available for B2B service businesses. For example, Klarna at Amazon checkout.
Merchant platforms:
These are typically merchant platforms with either a BNPL platform built-in (for example, Shopify) or integration with other providers like Klarna, Affirm and Square.
Multi-lender networks:
Merchant platforms and multi-lender networks typically have BNPL providers that they work with or white label themselves to offer a branded BNPL service. Examples of these are Shopify’s Klarna checkout and PayPal’s Xoom integration, which can take payments for consumers looking to buy online.
Bank credit cards:
The payments market has numerous bank credit card options that provide BNPL, often in combination with some other payment channels. For example, Chase and American Express instalment conversion.
White label providers:
These are the customised store credit cards (or BNPL) that you may have seen at certain stores (for example, IKEA) or online (for example, Airbnb).
While they generally don’t have multi-lender support, they do often provide white label customer acquisition – meaning that once a customer has shopped there with them before, they will be able to use their card again later on.
Buy Now Pay Later business models
Buy Now Pay Later Business Models, or BNPL models, have been around for years. These payment structures are commonly seen with credit cards and can also be applied to e-commerce models. They provide a way for consumers to pay for goods over time instead of immediately at the point of sale.
The Buy Now Pay Later business model has proven to be beneficial for businesses in terms of customer acquisition and retention. Several companies utilise BNPL business models, and there is no doubt that they will continue to grow into a large portion of e-commerce revenues worldwide.
The BNPL revenue model will only grow when businesses begin applying it correctly, and there is still room for improvement on that front. The three core aspects of the BNPL model are:
- Average Revenue per Customer
- Churn Rate
- Cost per Customer Acquisition
Let us now understand the different BNPL financial models and their profitability so that you can use them to develop your own unique approach:
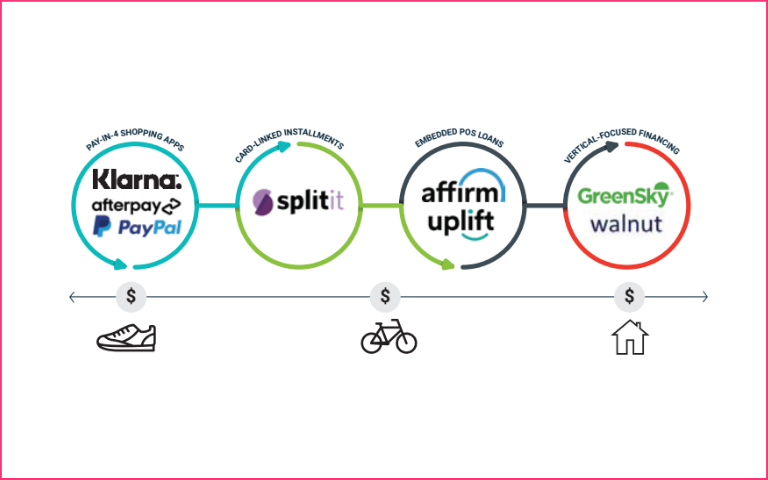
#1. Pay-in-4-Shopping apps (integrated shopping apps)
Integrated shopping apps have opened up a new revenue stream for retailers and given consumers another option for buying things online. The integrated shopping app model treats B.N.P.L. as more than just a credit product. It allows customers to split small transactions across multiple payment methods, e.g., a credit card and a PayPal account.
These apps have special features and functions to provide users with convenience when carrying out transactions on a single platform. Integrated shopping apps enable customers to seamlessly shop through various apps and buy via one-click payment or payment with mobile wallets.
Two examples of successful companies that have grown through their buy now pay later business models are Alibaba and Amazon. Both companies profit significantly from their BNPL business models by receiving interest on instalment payments made on their sites or through third-party financial institutions.
They also both take advantage of cross-selling opportunities by bundling loans into associated products. This strategy has worked out so well for Alibaba, they even created their own bank!
#2. Card-link instalments (off-card financing solutions)
This model primarily targets customers who still prefer to use their credit cards but need help paying them off over time. The company uses card-link instalments or off-card financing solutions (O.C.F.S.) as a means of offering customers access to merchandise without requiring a deposit.
With O.C.F.S., instead of asking for a deposit, businesses give consumers up to 60-90 days to pay their credit card balance in full. This model works especially well with big-ticket items that people would otherwise need to save up for, but is also effective for providing smaller purchases as well. Consumers can purchase and pay over time, enabling them to avoid paying interest on their credit card debt.
#3. Embedded P.O.S. loans (Virtual rent-to-own models)
The virtual rent-to-own model gives customers enhanced purchasing power, enabling them to own expensive items they might not otherwise be able to buy.
The benefit of a V.R.T.O. model is that it enables customers to acquire more expensive items than they could buy immediately. This is especially beneficial for customers with good credit, who might need to spend large amounts on things like home repairs or medical expenses but still want to save money on payments and interest rates.
The V.R.T.O. is an arrangement where consumers make payments for items they wish to own. For example, if a consumer wants to buy a T.V. but cannot afford it immediately, they can enter into a V.R.T.O. arrangement with an electronics store. The consumer could get that T.V. for ₹ 2000 per month for a few months, after which they would own it.
The V.R.T.O. buy now pay later business model is still in its infancy and offers many opportunities for entrepreneurs looking to get into rent-to-own business models. V.R.T.O. presents a whole new way for consumers to experience products and test them out before purchasing them, making it a natural fit for rent-to-own businesses.
There are no credit checks or long wait times: V.R.T.O.s are becoming increasingly popular. Through this, people who are unable or unwilling to make large upfront payments can access goods they would otherwise not purchase.
#4 Vertical-focused financing
Affordability is an important factor for consumers when purchasing new goods, which creates a huge market for financing. Vertical-focused financing model is meant for healthcare and home improvement areas, where transactions are large and have high margins.
This model is very similar to the way sales financing has traditionally worked, where the customer puts down a deposit. Then the company extends the credit to make up the difference.
For example, with some models of healthcare financing, customers pay 10% of their medical treatment upfront and then borrow money from a provider to cover 90% of treatment costs. This gives patients access to expensive surgeries or procedures they might not be able to afford on their own.
Tips for growing your business using BNPL
If you’re looking to expand your business, consider utilising BNPL business models. BNPL financial models can help give your customers access to purchasing decisions in ways traditional financing cannot.
Here are a few tips on implementing Bnpl financial models into your company.
- By utilising product-agnostic underwriting and credit delivery, you allow consumers to make their own choices about what they are paying for and enable them to take advantage of products based on who they are rather than just their financial history or spending behaviour.
- Although BNPL has typically been applied at checkout, it is important to integrate it across your digital ecosystem so customers can pay later after they have already determined what they want to purchase. Doing so helps increase brand loyalty and reach new customers.
- Consider how credit is scaled, as well as risk and economic variables.
- Try different BNPL revenue models based on the needs of your company.
Conclusion
There is a growing global trend for ‘Buy Now Pay Later’ business models. Through expanding online channels and social and digital media, consumer purchases are easier and quicker than ever before.
BNPL business models are thriving thanks to advances in technology, growing demand from consumers who have not traditionally been able to access credit and advancements in regulation. Because of these factors, there is a substantial global opportunity for retailers, especially those selling discretionary products.
About Nimbbl
Nimbbl is a BNPL powered one-click checkout to improve conversions for online commerce with reduced shopping cart abandonment rates.
FAQs
The concept of the “buy now pay later” is simple. Your customers can purchase without paying anything upfront, payments can be stacked and paid together or in equal instalments, eg pay in 3.
According to this B.B.C. report, more than 17 million people in the UK and 1 in 5 Americans have used the buy-now-pay-later model. That is a whopping number and is projected to increase in the coming years.
The global BNPL market size is expected to grow by USD 3.98 trillion by FY30, and with multiple BNPL business models to choose from, it is clear that businesses of all sizes are catching on to BNPL.
According to BusinessWire, the global bnpl market is forecast to grow by USD 41.83 billion during 2022-2026, accelerating at a CAGR of 29.36% during the projected period.